What sealing mechanisms are used in one-piece white protective suit to prevent contaminants from entering and maintain a secure seal?
Medical one-piece white protective suit typically uses a combination of sealing mechanisms to prevent contaminants from entering and maintain a seal. These mechanisms may include:
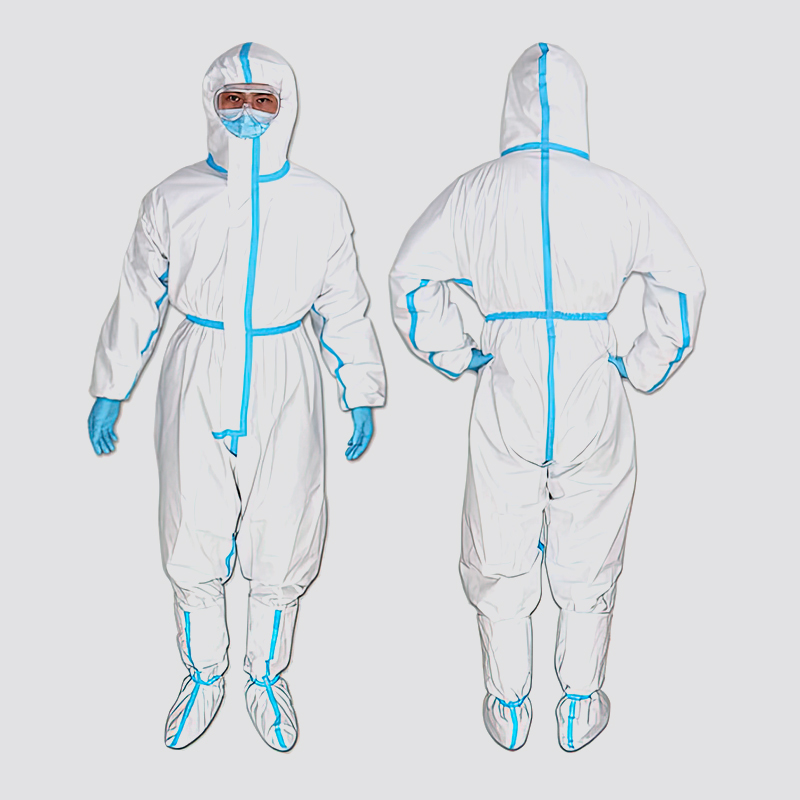
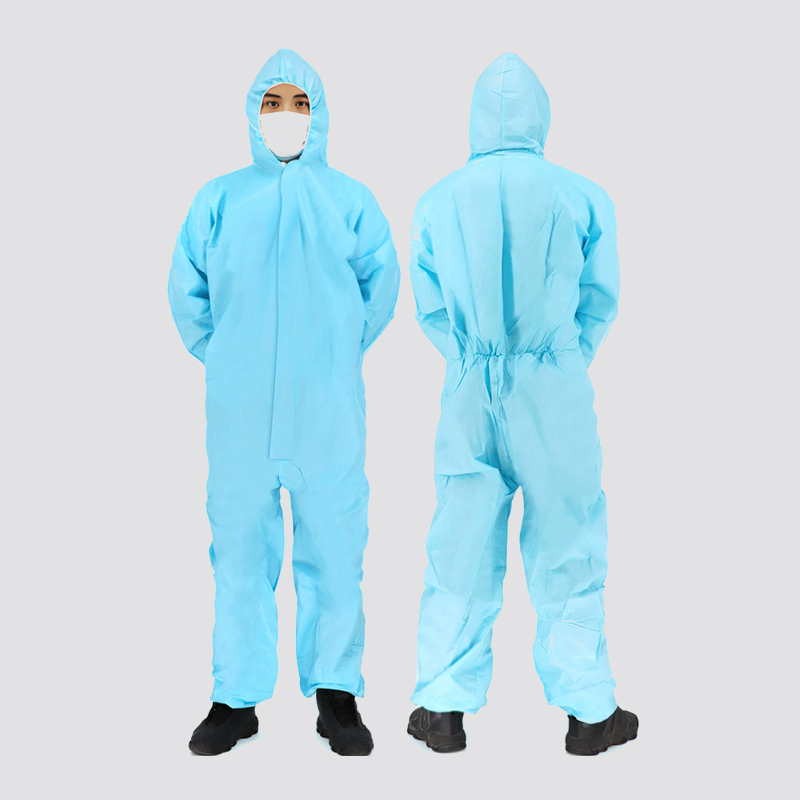
Elastic cuffs: Suit sleeves often have elastic cuffs that fit snugly around the wrist and prevent contaminants from entering the arm.
Thumb loop: Some suits have a thumb loop that holds the sleeves in place and completely covers the wrist. This ensures a continuous seal and prevents the sleeve from lifting upwards.
Zipper closure: Suits usually have zippers from chest to legs, creating a complete barrier to prevent contamination. Zippers must be properly sealed to maintain an airtight and secure seal.
Tapes or flaps: Some gowns may have tape or flaps that cover zippers and other potential entry points to create a tight seal and prevent possible contamination.
Hood and face seal: Suits may have an attached hood that covers the head and neck and is secured with elastic or drawstrings for a snug fit. The hood has a facial seal around the wearer's face to prevent contaminants from entering the suit through the head.
Shoe Covers and Boots: To protect your feet, medical protective equipment often comes with shoe covers or boots. These covers prevent contaminants from entering the foot area and maintain a full seal.
Integrated gloves: Some gowns have integrated gloves attached to the sleeves, eliminating potential gaps between the glove and sleeve that could allow contaminants to enter.
It is important for healthcare workers and individuals wearing medical one-piece white protective suit to ensure that all of these sealing mechanisms are used and calibrated correctly to maintain a secure seal and effectively prevent contaminants from entering.
How to properly dispose of one-piece white protective suit after use to prevent contamination?
To properly dispose of medical one-piece white protective suit after use and prevent contamination, follow these steps:
Safely remove one-piece white protective suit: Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer or healthcare provider and carefully remove one-piece white protective suit without touching contaminated exterior surfaces. Be sure to remove gloves, masks and other personal protective equipment (PPE) first and avoid touching the front of the gown.
Double baggage: Double bag your used gown to safely contain any potential contaminants. Use a sturdy plastic bag that can be sealed to prevent leaks.
Secure Seal: Close the opening of the first bag and seal. Then put it into a second bag and seal it. This provides an extra layer of protection against potential exposure.
Label: Use a permanent marker to clearly label the bag "Biohazard" or "Clinical Waste" to ensure proper handling during disposal.
Notify Appropriate Parties: Notify the appropriate medical facility or biomedical waste management agency of the presence of biohazardous waste so that appropriate transportation and disposal can occur.
Hand Hygiene: After disposing of old one-piece white protective suit, perform thorough hand hygiene with soap and water for at least 20 seconds or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
Please note that specific guidelines may vary depending on your location and local regulations. Therefore, be sure to follow the disposal procedures prescribed by your healthcare provider or consult your local government for proper disposal methods.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español